A Real-Time Stability Control Method Through sEMG Interface for Lower Extremity Rehabilitation Exoskeletons
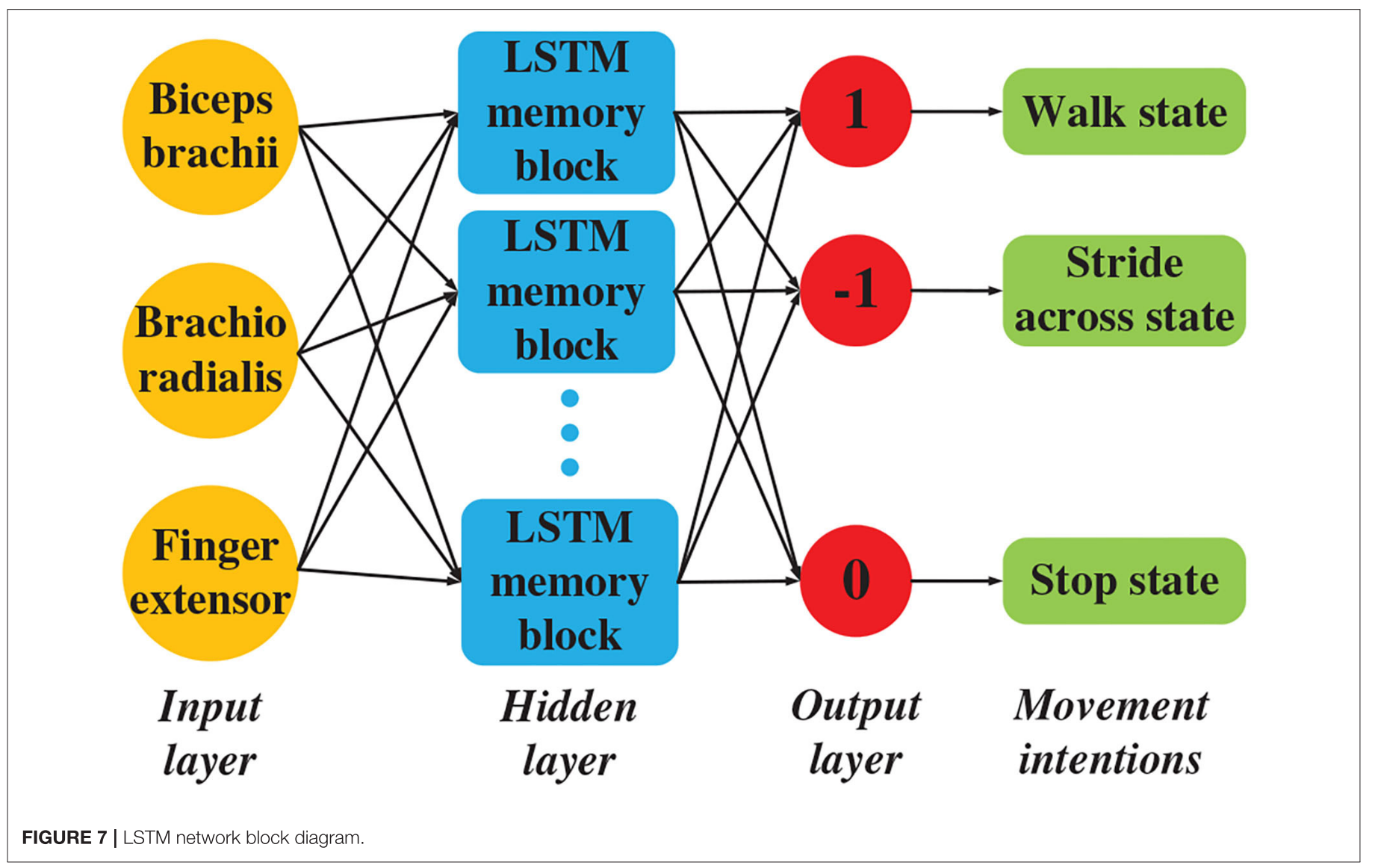
intention定义: walk/stride across/stop state
Research question
- analysis of gait planning based on a human kinematics model and real-time motion stability based on the zero-moment point (ZMP).
- a neural interface based on sEMG to achieve motion intention recognition and muscle fatigue estimation.
- to verify the stability of human–exoskeleton system and ergonomic effects of the proposed gait switching method by organized experiments.
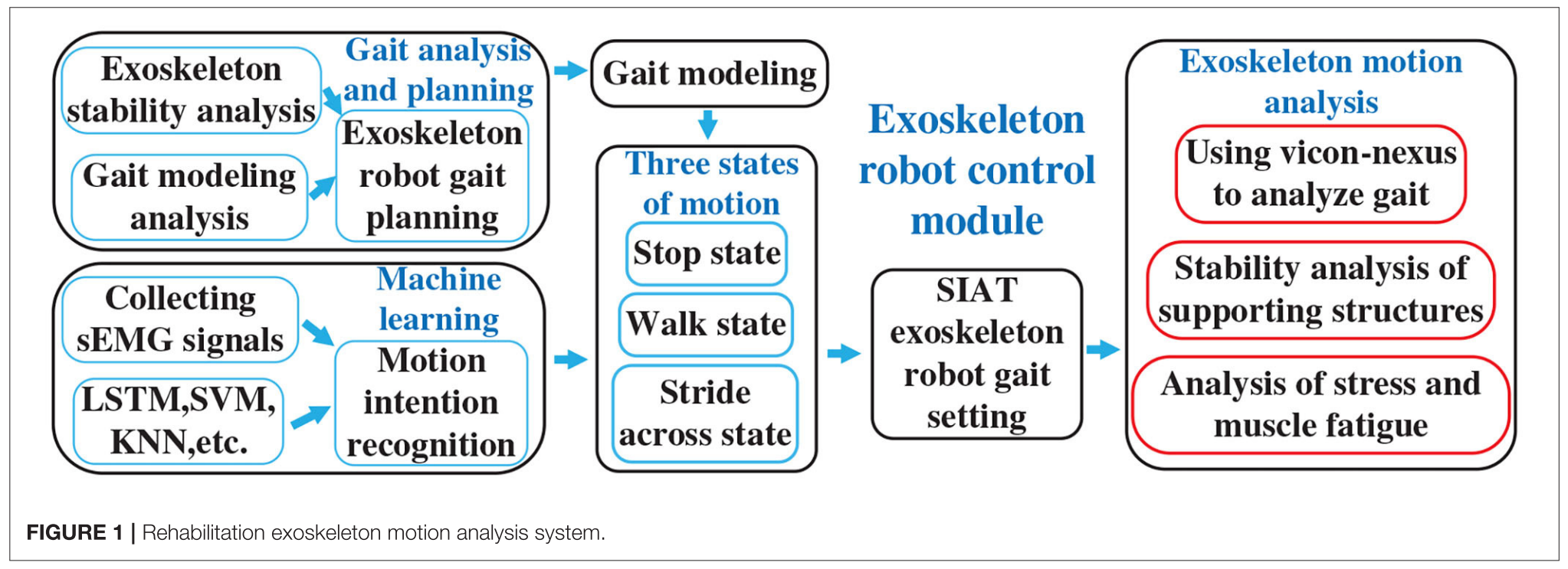
Introduction
-
一些商用外骨骼
Exoskeleton robots require the human interface to provide walking stability so that it may function as a flexible assistant. Such robots have been developed by commercial companies including Rewalk (Talaty et al., 2013), Ekso Bionics (Baunsgaard et al., 2018), Ailegs (Chen et al., 2018), and MaiBu BEAR H1. Exoskeleton robots especially require the walking stability as far as possible so as to provide flexible assistant. The Hybrid Assistive Limb (HAL) (Shimizu et al., 2019), which takes advantage of sEMG in control strategy, was designed by the robotics company Cyberdyne (Yilmaz et al., 2018).
-
研究机构和大学的外骨骼
Sogang University in Korea developed a exoskeleton namely SUBAR (Chen et al., 2013; Hwang and Jeon, 2018), which could estimate the muscular torque of its wearer. Singapore’s Nanyang Technological University (Mertz, 2012) and Harvard University (Abe et al., 2018) have also made solid progress in the development of assisted exoskeletons. The Chinese University of Science and Technology designed an exoskeleton robot driven by a servo motor (Li et al., 2019) and developed a fuzzy algorithm for lower extremity exoskeleton (Huang et al., 2016a). The exoskeleton team of H. C. from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China have developed exoskeletons for paraplegia (Huang et al., 2018), hemiplegia patients (Peng et al., 2020), and human-power augmentation (Huang et al., 2016b, 2019). The exoskeleton group at the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed the fourth generation of the SIAT exoskeleton robot. With four degrees of freedom (DoFs), this exoskeleton robot has successfully enabled persons with disabilities to stand up and walk independently (Liu et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2018a).
-
While investigating the existing exoskeleton control methods, we found very few studies that have examined the minimum force requirements into the control scheme by the wearer. We also found scarce consideration for the state of the wearer while operating a lower limb exoskeleton.
Methods
Gait Planning
We initially treat these two joints as two points and draw the trajectories of these points during the walking process to determine the trajectory approximating the sine function (Chen et al., 2019)
Motion Intention Recognition
Muscle Fatigue Estimation
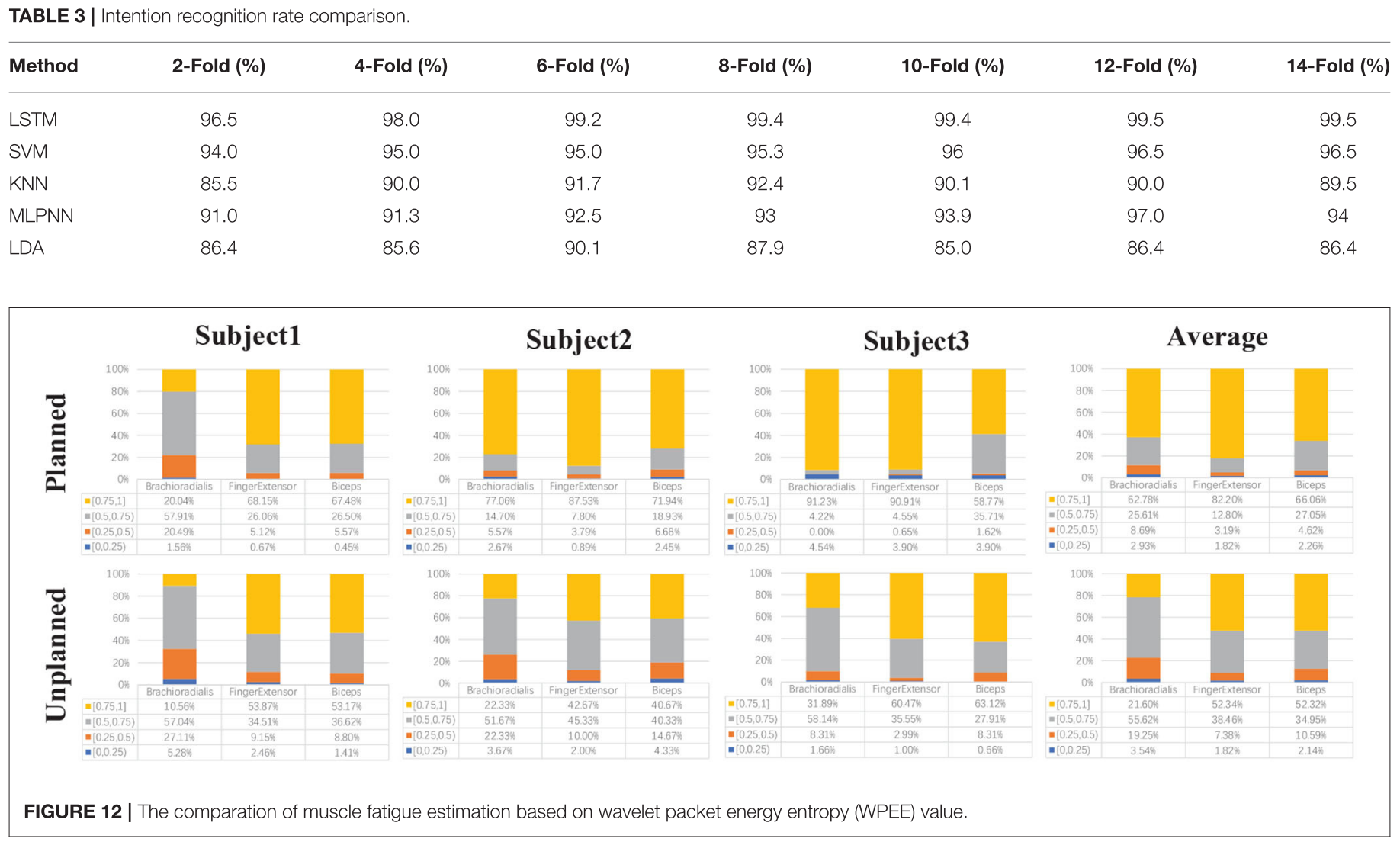
the wavelet packet energy entropy (WPEE)
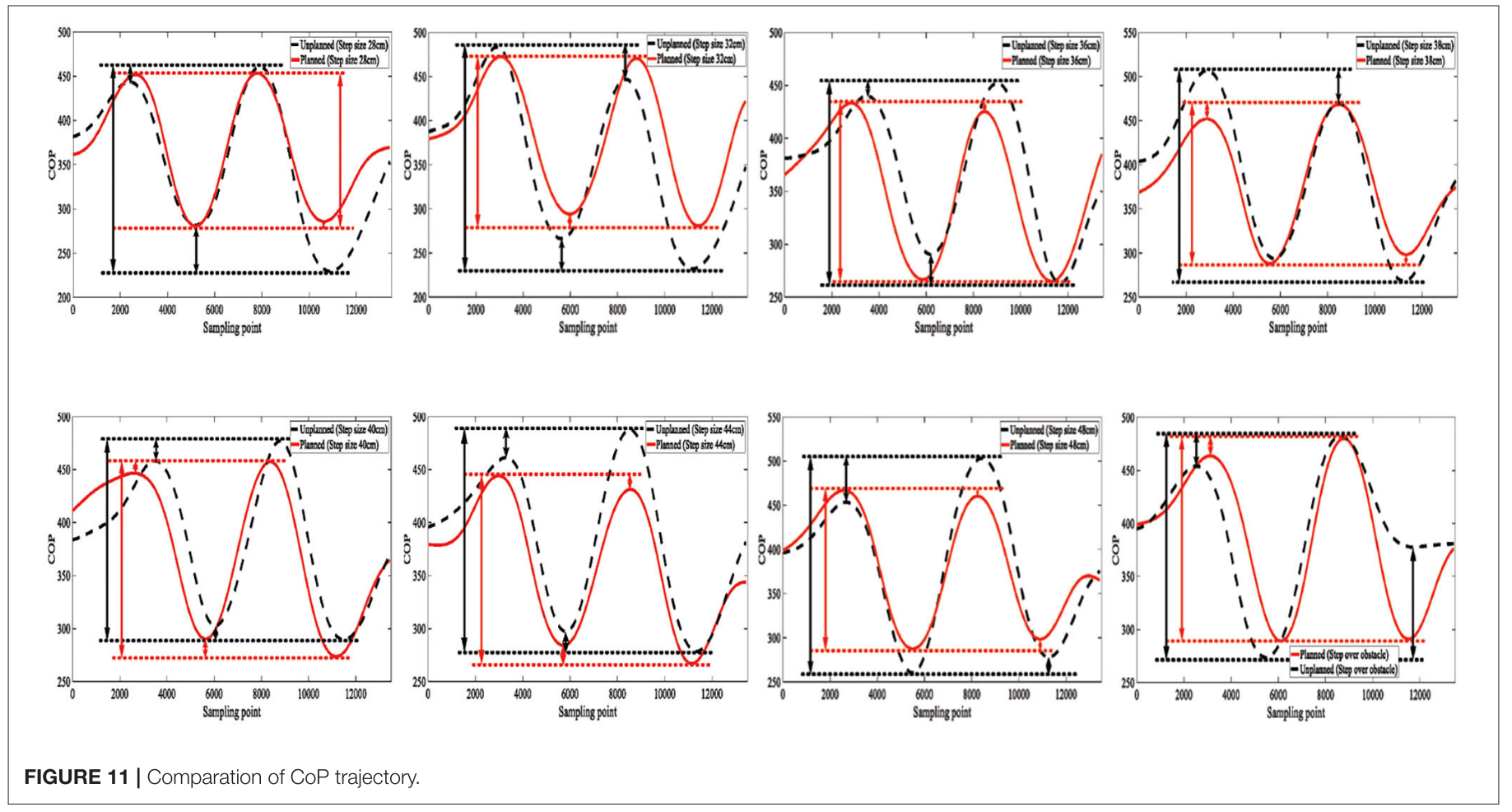
Results
Thoughts/Comments
这个虽然用到了COP/ZMP,但是因为是康复外骨骼有俩拐杖应该不能直接用它这个公式,但是计算方法可以看一下
这通篇读下来也没看出来哪里control了啊,就三个模式检测出来直接上对应的机器状态,不愧是康复型