Multi-sensor based human motion intention recognition algorithm for walking-aid robot
intention定义:velocity; 这里表征为一个自定概念IM
Research question
A multi-sensor(force sensors and LRF; for both lower and upper limbs) based human motion intention recognition algorithm for walking-aid robot.
Introduction
- assistive rehabilitation robots: PAMM, Walking Helper, HAL, Omni RT Walker-II (ORTW-II)
- 简略说了一些human motion estimation methods
Methods
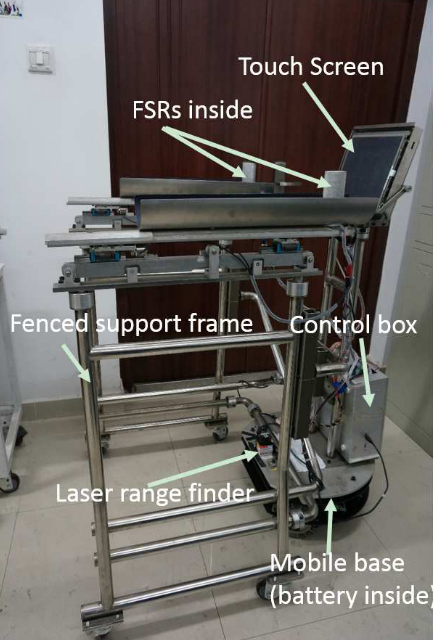
- Sensors: push-pull force sensors and LRF(Laser Range Finder)
-
LRF: Range Segmentation, Identification of Circle, Leg detection, Intention detection
-
using the center position of line segment which consists of two legs position to estimate human motion intention:
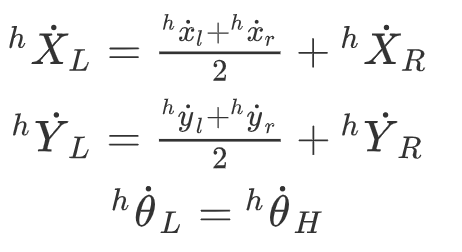 {h} and {r} are local coordinate systems, which are fixed on the human and robot respectively.
{h} and {r} are local coordinate systems, which are fixed on the human and robot respectively.
-
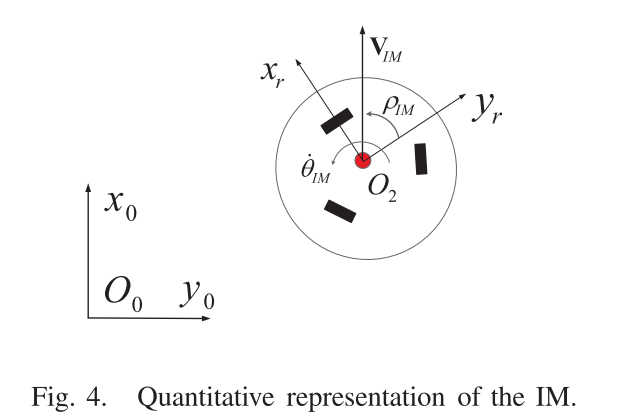
Define intentional motion (IM) to describe the human walking intention during using the walking-aid robot
$S_{I M}(n)= \{\dot{\theta}_{I M}(n), \rho_{I M}(n), v_{I M}(n)\}$(角速度、线速度)
-
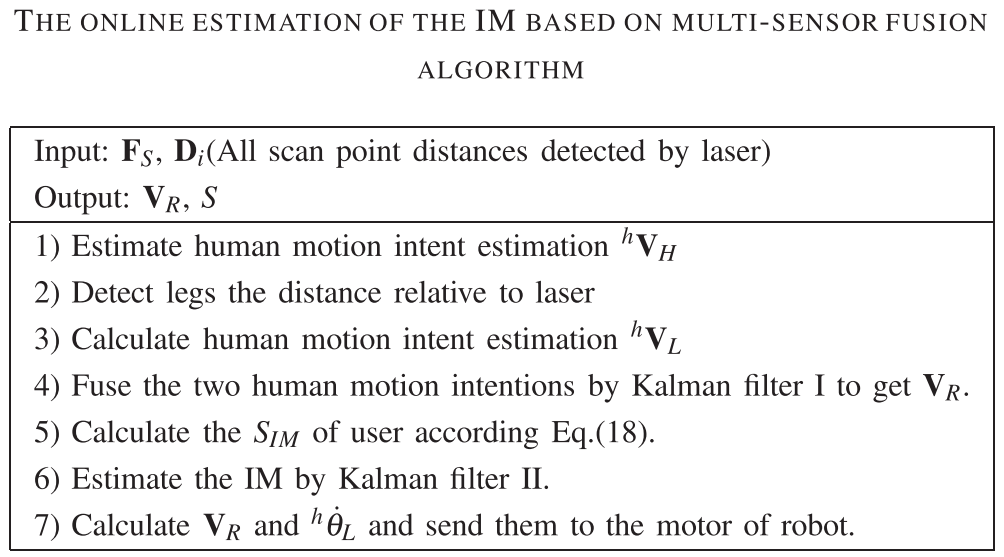
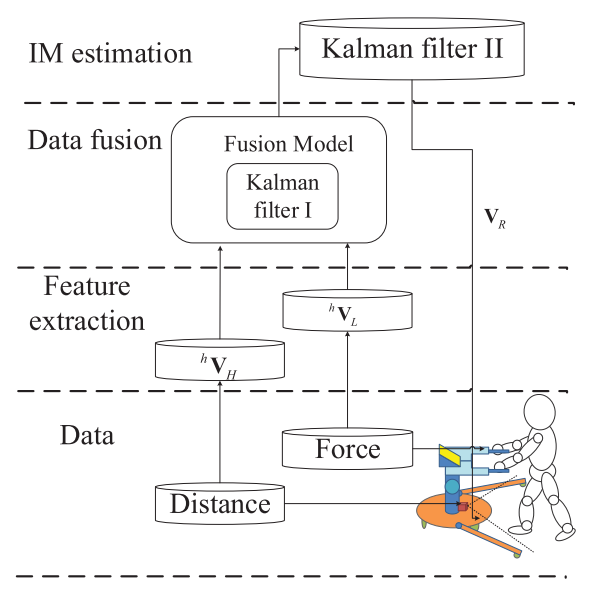
Multi-sensor fusion: Kalman filter
$^h \mathbf{V}_{H} $ $^h \mathbf{V}_{L}$: human intent motion velocities estimated by force sensors and laser ranger finder respectively; input of Kalman filter
$\mathbf{V}_{R}=[\dot{x}_{R}\ \dot{y}_{R} ]^{T} $: output of Kalman filter; filtered human motion intention
-
Online Estimation of the IM: different dimension of conventional Kalman filter