| Author | Title | Sensor | Terrain | Method | Online/Offline | Accuracy | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface effects on dynamic stability and loading during outdoor running using wireless trunk accelerometry | three outdoor training surfaces (concrete road, synthetic track and woodchip trail) | 1.Dynamic postural stability (tri-axial acceleration root mean square (RMS) ratio, step and stride regularity, sample entropy), dynamic loading (impact and breaking peak amplitudes and median frequencies), as well as spatio-temporal running gait measures (step frequency, stance time) were derived from trunk accelerations 2.generalized estimating equations (GEE) analysis |
Offline | 主要是统计学分析;用了variability的variability作为特征;涉及了一点降维 | |||
| P.Ippersiel, V.Shah, P.C.Dixon | The impact of outdoor walking surfaces on lower-limb coordination and variability during gait in healthy adults | flat (paved sidewalk); irregular (cobblestone, grass); sloped (slope-up, slope-down); and banked (banked-right, banked-left) surfaces | CRP analysis determined inter-joint coordination and variability using MARP and DP, respectively. One-way repeated measures ANOVAs tested surface effects. Post-hoc Bonferroni adjusted surface comparisons were assessed. | Offline | 主要是统计学分析;用了variability的variability作为特征;涉及了一点降维 | ||
| Daniel B. Kowalsky, John R. Rebula, Lauro V. Ojeda | Human walking in the real world: Interactions between terrain type, gait parameters, and energy expenditure | a global positioning system (GPS) device, and one inertial measurement unit (IMU) per foot |  5: Sidewalk, Dirt, Gravel, Grass, and Woodchips |
LDA features: (mean, RMS)virtual clearance, stride height, stride length, lateral swing, speed; (RMS)stride width |
Offline | 45/50 | 主要是统计学分析;用了variability的variability作为特征;涉及了一点降维 |
| What Lies Beneath One’s Feet? Terrain Classification Using Inertial Data of Human Walk | IMU (chest and lower back) | 6: carpet, concrete floor, grass, asphalt, soil, and tile | RF SVM 94 tempo-spectral features, of which 110 features were computed from the time domain (T) and 84 features were computed from the frequency domain (F). 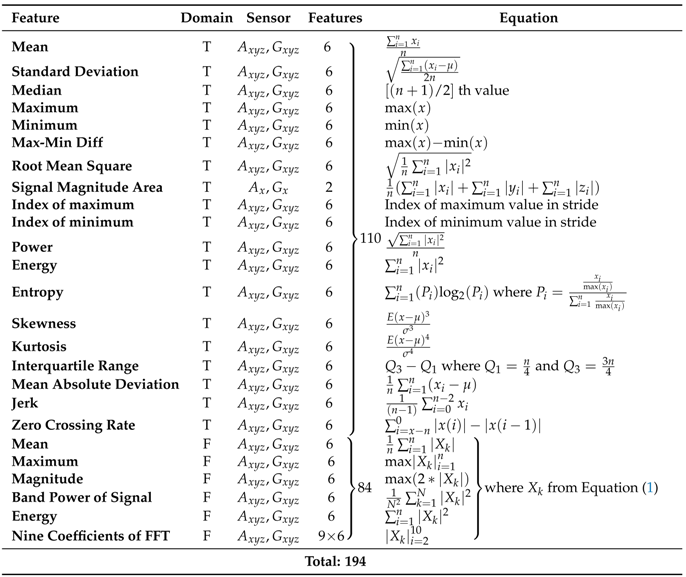 |
Offline | 就是提特征丢进分类器里 | ||
文献中的一些其他总结
| Category | Year | Sensor | Classifier | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anastrasirichai [11] | Vision | 2015 | Camera | SVM |
| Dornik [6] | Vision | 2017 | Camera | Random Forest |
| Ma et al. [9] | Vision | 2017 | Camera | SRC |
| Christie et al. [22] | Acoustic | 2016 | Microphone | SVM |
| Valada et al. [15] | Acoustic | 2018 | Microphone | Deep Learning |
| Ojeda [13] | Robotics | 2006 | IMU, Motor | ANN |
| Giguere et al. [4] | Robotics | 2011 | Tactile | ANN |
| Wu et al. [3] | Robotics | 2016 | Tactile | SVM |
| Manduchi et al. [1] | Autonomous off-road driving | 2005 | Ladar & Camera | Gaussian Process |
| Lu et al. [20] | Autonomous off-road driving | 2009 | Laser | PNN |
| Hu et al. [33] | Human Gait | 2018 | IMU | LSTM |
| Diaz et al. [34] | Human Gait | 2018 | Camera, IMU | BoW model |